Screen printing
What is Screen Printing?
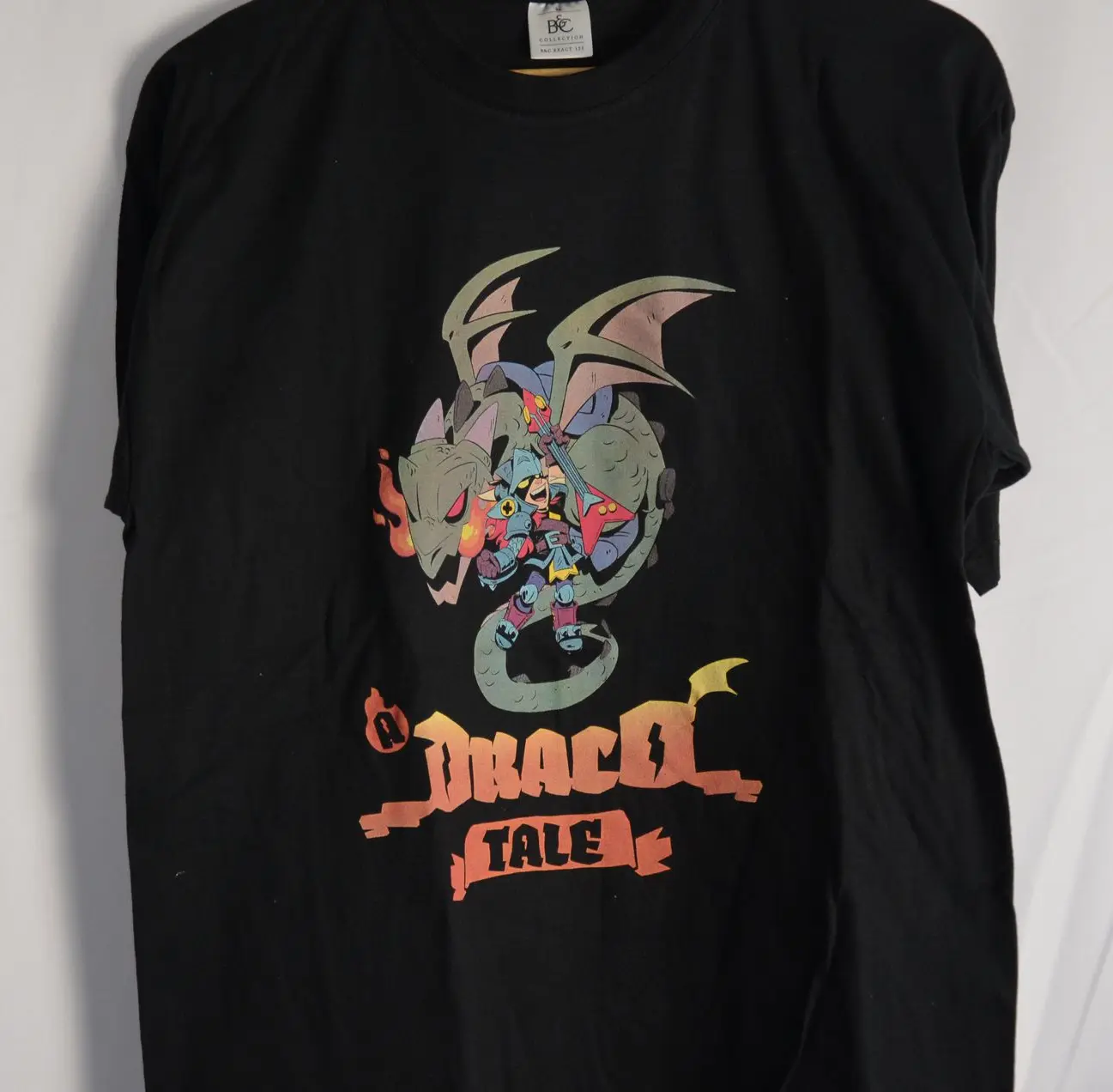
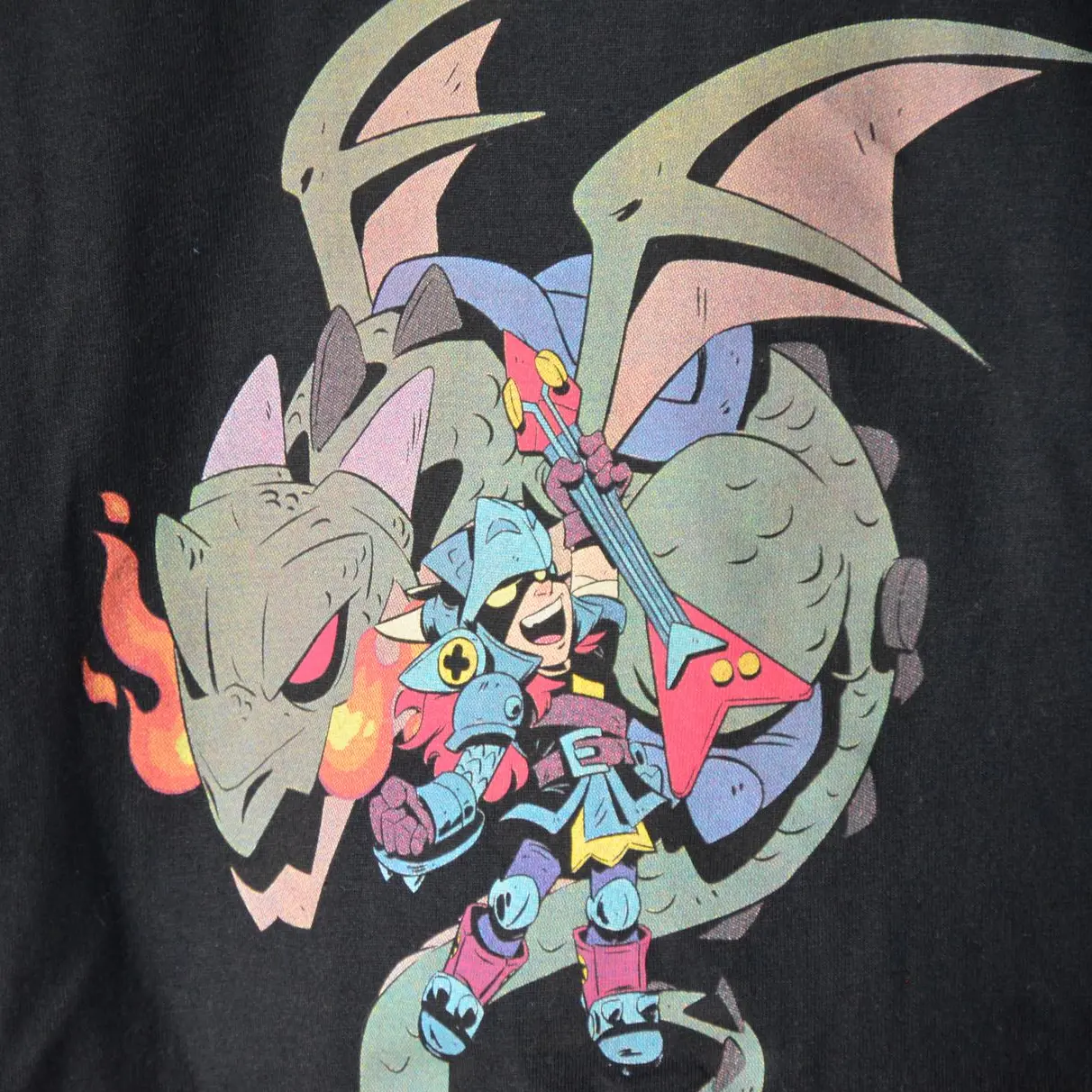
Screen printing, also known as serigraphy, is a versatile technique that uses a mesh stencil to apply ink onto surfaces like fabric. It allows for intense, opaque colors and is known for producing durable, high-quality prints.
This ancient method involves applying each color layer one at a time, with a separate stencil for each. It’s widely used today for textiles like t-shirts and tote bags, but also works on materials like paper, wood, and ceramics. While digital printing is common, screen printing remains favored for its reliability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness.
What's the Process?
1. Design Preparation
Creating the Artwork: The process begins with preparing the artwork or design that will be printed. For a one-color screen print, the design is often simple, involving solid areas of one color without gradients.
Converting to Monochrome: The artwork is converted into a black-and-white image where black areas represent where the ink will be applied. This is essential for creating the stencil.
2. Creating the Screen
Screen Selection: A screen is selected based on the mesh count, which determines the level of detail and ink thickness. Lower mesh counts are used for bold designs, while higher counts are used for finer details.
Coating with Emulsion: The screen is coated with a light-sensitive emulsion. This emulsion will harden and create a stencil after exposure to UV light.
Exposing the Screen: The black-and-white design is printed on a transparent film and placed on the emulsion-coated screen. The screen is then exposed to a strong UV light source. The light hardens the emulsion where it is exposed, and the areas blocked by the design remain soft.
Washing Out the Screen: The screen is washed with water, removing the unexposed (soft) emulsion and leaving a stencil of the design. This stencil allows ink to pass through only the areas where the emulsion has been removed.
3. Setting Up for Printing
Aligning the Screen: The screen is mounted on a printing press. The fabric (e.g., a t-shirt) is placed on the platen or printing surface and aligned to ensure precise placement of the design.
Choosing the Ink: The appropriate ink is selected for the fabric type. For one-color prints, a single ink color is used.
4. Printing the Design
Applying the Ink: Ink is poured onto the screen. A squeegee is used to pull the ink across the screen, pressing it through the mesh and onto the fabric below. This is done in one smooth motion to ensure even ink coverage.
Flash Curing (if needed): Depending on the ink type and fabric, the print may be flash-cured (partially dried) between multiple passes of ink to build up the print or ensure opacity.
5. Curing the Print
Heat Curing: Once the ink is applied, the fabric is moved through a conveyor dryer to cure the ink. The heat bonds the ink to the fabric, ensuring durability and resistance to washing.
Curing Temperature and Time: The temperature and curing time depend on the type of ink and fabric. Typically, the ink is cured at temperatures around 160°C for 1-2 minutes.
6. Final Inspection and Finishing
Quality Check: After curing, the printed items are inspected for quality. This includes checking the print for consistency, alignment, and any defects.
Finishing Touches: Any additional steps, such as trimming threads or folding garments, are completed before packaging.
Textile
One Colour
Pros | Cons |
Cost-Effective: One-color screen printing is economical, especially for larger runs, as it requires fewer materials and less setup time compared to multi-color prints. | Design Complexity: While screen printing excels with bold, simple designs, it might not capture intricate details or gradients as well as other methods like digital printing. |
Bold and Vibrant: This method is perfect for designs that require solid, bold colors. The ink is applied thickly, ensuring vibrant and long-lasting prints. | Setup Time: The setup process, including creating screens and preparing the press, is time-consuming. However, once set up, it’s very efficient for large quantities. |
Versatility: Screen printing works well on a variety of fabrics and materials, making it a versatile option for different types of apparel and textiles. | Environmental Impact: Screen printing uses chemicals for the emulsion and cleaning processes. Using eco-friendly inks and recycling materials can help mitigate the environmental impact. And at Inkoo, 100% of our inks are waterbased. |
Durability: The ink used in screen printing is durable and withstands multiple washes without fading or cracking. |
Multicolour Screen Printing
Pros | Cons |
Vibrant and Long-Lasting Colors: Multicolor screen printing can produce very bright and durable colors that do not fade easily. | Setup Time and Cost: Initial setup for multicolor printing is more time-consuming and expensive due to the need for separate screens for each color. |
High Quality and Detail: This technique allows for high-resolution images with fine details, making it suitable for complex designs. | Complexity: More colors mean more screens and more registration steps, which can increase the complexity of the process. |
Versatility: Can be used on a wide range of materials including textiles, paper, wood, glass, ceramics, and more. | Material Limitations: Not all materials are suitable for screen printing, and the choice of ink needs to be compatible with the substrate. |
Durability: The prints are resistant to washing and wear, especially on fabrics, making them ideal for items that will be used frequently. | Environmental Impact: While many companies use eco-friendly inks (us at Inkoo), traditional screen printing can involve chemicals that are harmful to the environment. |
Cost-Effective for Large Runs: Economical for large volume production, as the cost per unit decreases with higher quantities | Skill Required: Requires skilled labor to ensure proper alignment (registration) of each color and to manage the printing process. |
Discharge printing
What is Discharge printing?
Discharge printing is a textile printing technique that removes the dye from fabric, creating a design by essentially bleaching the color out of the material. This process can be followed by adding a new color to the bleached area. Here’s how it works:
- Preparation: The fabric is dyed with a reactive dye that can be deactivated (discharged).
- Discharge Paste: A discharge paste, which contains a reducing agent like zinc formaldehyde sulfoxylate, is prepared. This paste can also include pigments if a new color is desired.
- Application: The discharge paste is applied to the fabric using a screen-printing method.
- Heat Activation: The printed fabric is then subjected to heat, typically in a curing oven, which activates the discharge agent. This process removes the dye from the fabric in the printed areas.
- Washing: The fabric is washed to remove any remaining chemicals and to reveal the final design.
Pros | Cons |
Soft Hand Feel: Unlike traditional screen printing, discharge printing leaves the fabric feeling soft and natural since it removes the dye rather than adding ink on top. | Fabric Specificity: Works best on 100% cotton fabrics. Blends and synthetic fibers do not discharge well. |
Vibrant Colors: The technique can produce vibrant colors on dark fabrics, which are usually harder to achieve with other printing methods. | Color Limitations: The initial fabric dye must be reactive and capable of being discharged. Not all dyes are suitable. |
Breathable Prints: Since the dye is removed rather than layered, the print remains breathable, which is ideal for wearable items. | Chemical Use: Involves chemicals that can be hazardous, requiring proper handling and disposal. |
High Detail: Allows for intricate designs with fine details. | Environmental Impact: Needs careful management of chemical waste to minimize environmental harm. (which is well handled at Inkoo) |
Durability: The prints are highly durable and can withstand repeated washing without significant fading. | Complex Process: Requires precise control of conditions like temperature and timing during the heat activation stage. |
Puff printing
What is Puff printing ?
Puff printing is a special screen printing technique that adds a raised, three-dimensional texture to the printed design. This effect is achieved by using an ink that expands when exposed to heat. Here’s how it works:
- Preparation: A special puff additive is mixed with our regular waterbased ink. This additive causes the ink to expand when heated.
- Application: The ink mixture is applied to the fabric using a screen-printing method. The design is printed as usual, but the puff ink is typically thicker to ensure a good 3D effect.
- Heat Activation: The printed fabric is then cured in a heat press or conveyor dryer. The heat causes the puff additive to activate and expand, creating a raised, textured effect.
- Final Product: The result is a three-dimensional, tactile design that stands out from the fabric surface.
Pros | Cons |
| Unique Texture: Creates a raised, textured effect that adds a unique, tactile element to the design. |
Ink
Mixing: Requires
precise mixing of the puff additive with the ink to achieve the desired effect. |
|
Visual
Interest: The
3D effect makes designs more eye-catching and adds a layer of depth. | Heat Sensitivity: The puff effect is dependent on proper curing; incorrect heat settings can result in poor expansion or damage to the design. |
|
Versatility:
Can
be combined with other printing techniques for varied effects. |
Design
Limitations: Best
suited for bold, simple designs; intricate details may not puff evenly. |
|
Durability:
The
raised design is durable and can withstand regular washing and wear. |
Thickness
Control: The
thickness of the ink layer must be carefully controlled to ensure uniform
puffing. |
| Customization: Offers a way to make designs stand out and can be used for special editions or limited runs. | Fabric Suitability: Works best on fabrics that can withstand the heat curing process, typically cotton or cotton blends. |
Neon printing
What is Neon printing?
Neon printing is a screen printing technique that uses neon or fluorescent inks to create bright, eye-catching designs. These inks are made with pigments that reflect ultraviolet light, giving them a glowing appearance under both regular and UV lighting. Here’s how it works:
- Ink Selection: Special neon or fluorescent inks are selected. These inks are typically more vibrant than regular inks and can glow under UV light.
- Screen Preparation: The screen is coated with a photosensitive emulsion and exposed to light through a film positive, creating the stencil for the design.
- Printing: The neon inks are applied to the substrate using the prepared screen. Multiple layers may be applied to achieve the desired brightness and opacity.
- Curing: The printed item is cured using heat to ensure the ink adheres properly and remains durable.
- Final Product: The result is a vibrant, eye-catching design that stands out, especially in low light or under UV lighting.
Pros | Cons |
|
High
Visibility: Neon
prints are extremely bright and eye-catching, making them ideal for designs
that need to stand out. | Ink Properties: Neon inks can be thicker and more difficult to work with than regular inks, requiring adjustments in the printing process. |
|
Unique
Aesthetic: Offers
a distinctive look that can be appealing in fashion, promotional materials, and
artistic projects. |
Color
Matching: Achieving
consistent color across different print runs can be challenging due to the
nature of neon pigments. |
|
Versatility:
Can
be used on a wide range of materials, including textiles, paper, and plastics. |
Durability:
Neon
prints may not be as durable as traditional inks, particularly under prolonged
exposure to sunlight, which can cause fading. |
| UV Reactive: Glows under blacklight, adding an extra layer of visual interest for events and environments with UV lighting. |
Cost:
Neon
inks are generally more expensive than regular inks, which can increase
production costs. |
| Customization: Can be combined with other printing techniques for a variety of effects and designs. |
Limited
Use: Best
suited for specific applications where bright, glowing colors are desired; not
always suitable for more subdued or professional designs. |
Softshell printing
What is Softshell/ nylon printing?
Softshell printing is a specialized technique used to print designs onto softshell fabrics, which are typically used for outdoor and performance wear. Softshell materials are often composed of a blend of polyester and elastane, providing a combination of water resistance, breathability, and flexibility. Printing on these materials requires specific inks and methods to ensure durability and maintain the fabric's properties. Here’s how it works:
- Material Selection: Softshell fabrics are chosen for their unique properties, such as water resistance and flexibility.
- Ink Selection: Special inks that adhere well to synthetic fibers and stretch with the fabric are selected. These inks are often plastisol or silicone-based.
- Surface Preparation: Nylon surfaces may require pre-treatment, such as cleaning or application of a bonding agent, to ensure good ink adhesion.
- Screen Preparation: The screen is coated with a photosensitive emulsion and exposed to light through a film positive to create the stencil for the design.
- Printing: The ink is applied to the softshell fabric using the prepared screen. The printing process must be carefully controlled to avoid compromising the fabric's performance characteristics.
- Curing: The printed fabric is cured using heat to ensure the ink adheres properly and remains durable without affecting the fabric's flexibility and water resistance.
- Final Product: The result is a high-quality print that maintains the softshell fabric's functionality and durability.
Here are a few links to our blog, if you are interested in a more thorough explanation about Softshell fabric, the best printing techniques we can use on it, the occasions of wear or a comparison with polar fleeces.
Pros | Cons |
| Durable Prints: The inks used in softshell printing are designed to withstand the elements, ensuring long-lasting prints even on performance wear. |
Ink
Compatibility: Not
all inks work well with softshell fabrics; specific inks that bond well with
synthetic fibers are necessary. |
|
Flexibility:
The
prints retain the fabric’s stretch and flexibility, making them suitable for
activewear. |
Complex
Process: Requires
precise control over the printing and curing process to maintain the fabric's
performance characteristics. |
|
Water
Resistance: Softshell
fabrics often maintain their water-resistant properties even after printing. |
Cost:
Special
inks and careful handling can increase production costs compared to printing on
standard fabrics. |
|
High-Quality
Finish: Produces
vibrant and detailed designs that look professional and appealing. | Environmental Factors: Must consider the impact of weather and wear on the printed design, ensuring it remains intact and vibrant over time. |
| Versatile Applications: Suitable for a range of outdoor and performance garments, including jackets, vests, and pants. | Skill Required: Effective softshell printing requires skilled labor to ensure high-quality results without damaging the fabric. |
Goodies
When it comes to creating eye-catching and durable promotional items, screen printing is the go-to technique for customizing goodies like mugs, pens, tote bags, and keychains.
Screenprinting
Screenprinting on goodies: how does it work?
Screen printing on goodies involves applying designs to various promotional items and merchandise such as mugs, pens, tote bags, keychains, and more. This method uses a mesh screen, ink, and a stencil to transfer the design onto the chosen items. It is basically the same process as with apparel. Here’s how it works:
- Item Selection: The items (goodies) to be printed are chosen, which can range from textiles to plastics, ceramics, and metals.
- Screen Preparation: A screen is coated with a photosensitive emulsion and exposed to light through a film positive, creating the stencil for the design.
- Ink Selection: Depending on the material of the item, different inks are selected (e.g., water-based inks always suitable for the selected products).
- Printing: The ink is pushed through the mesh screen onto the item using a squeegee. Each color in the design requires a separate screen and application process.
- Curing: The printed items are cured using heat or UV light to ensure the ink adheres properly and remains durable.
- Quality Control: The printed items are inspected for quality to ensure the design is properly applied and free of defects.
- Final Product: The result is a high-quality, durable print on a wide variety of promotional items and merchandise.
Pros | Cons |
|
Versatility:
Screen
printing can be applied to a wide range of materials, making it ideal for
diverse promotional items. | Setup Time and Cost: The initial setup for screen printing can be time-consuming and costly due to the need for separate screens for each color. |
|
Durability:
The
prints are robust and can withstand wear and tear, ensuring the design lasts
over time. |
Material
Limitations: Not
all materials are suitable for screen printing, and ink selection must be
compatible with the substrate. |
| High Quality: Produces vibrant and detailed designs that stand out on the items. |
Complexity
for Multicolor Designs: Each
color requires a separate screen and alignment, increasing the complexity of
the process. |
|
Cost-Effective
for Large Runs: Economical
for bulk production, reducing the cost per unit as the quantity increases. |
Environmental
Impact: Traditional
screen printing involves chemicals and inks that require proper handling and
disposal to minimize environmental harm. |
| Customizability: Allows for unique and customized designs tailored to specific promotional needs. |
Skill
Required: Effective
screen printing requires skilled labor to ensure high-quality results and
proper handling of the materials and equipment. |